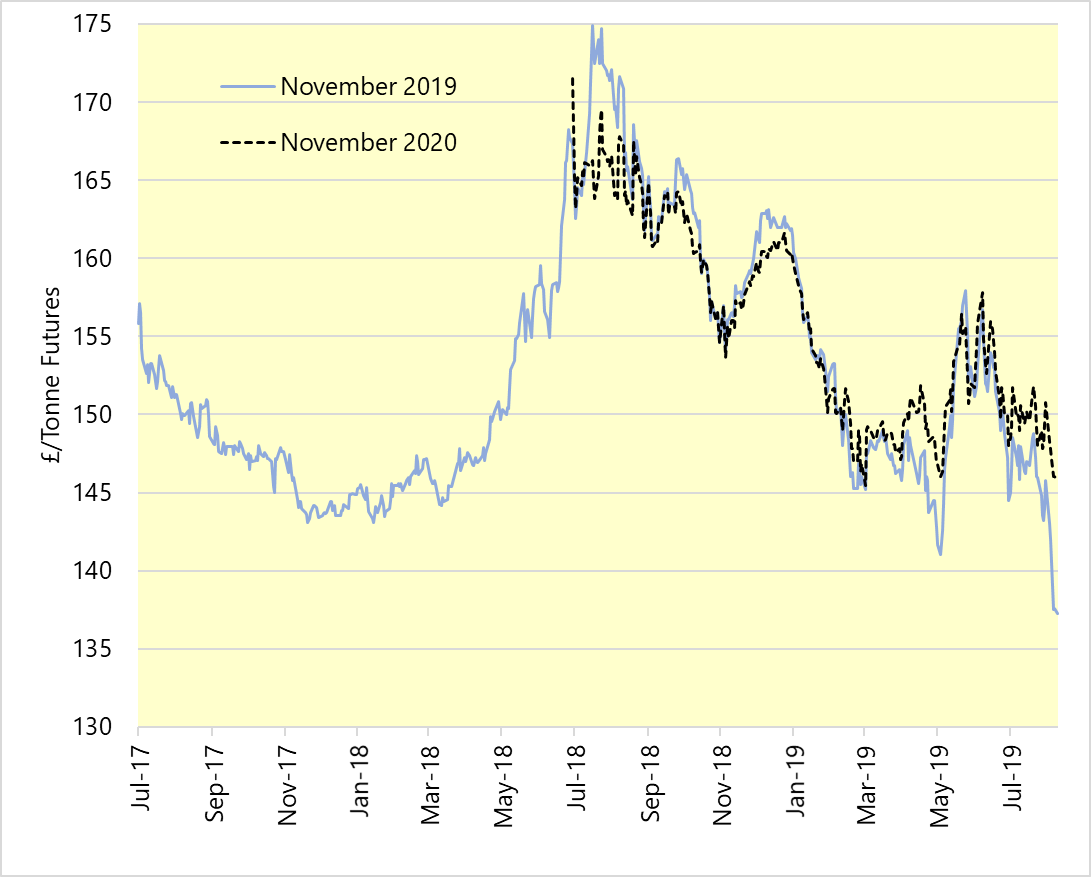
Old Crop
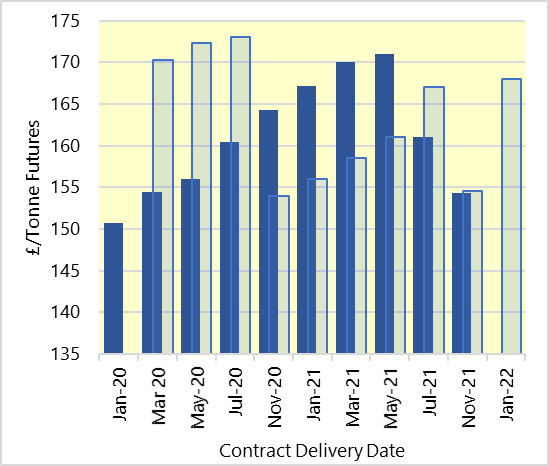
Technical changes: Towards the end of the wheat marketing season, the impact of the fundamentals of grain supply and demand change, with some factors taking on greater impact, others less. Attention then turns to new crop, and the fundamentals affecting it. The increasing amount of information over the emerging new crop overtakes the dwindling and ageing information about the remaining old crop, of which little remains uncommitted in barns. This increases the impact from new crop fundamentals. Secondly, the volume of new crop wheat being traded, which is rising all the time surpasses the declining volumes traded of old crop. This accelerates when the last old crop futures market expires as is the case now as we enter May. Market fluidity also declines when futures markets are not available. The technicalities of closing contracts held becomes a physical issue either having to physically deliver them or close the position.
Fundamental changes: Grazing animals have gone to pasture, so feed grain requirements have fallen sharply as is often the case in spring.
Demand for bread rocketed in the first days of lockdown, fuelled largely by thoughtless panic-buying. It has settled at about 115% of normal demand which millers and bakers are managing to meet. Bagged flour was considered a secondary priority as it is less critical to consumers and slower to reach them, more wasteful than bakers baking bread, more expensive but less profitable to the supply chain, and the paper bags were in very short supply. It is now coming back on-stream thanks to good communications throughout the supply chains. Nabim published a map of available flour outlets.
Poultry consumption has risen, and produces have adjusted their feeding regimes to fit in with their new supply chain requirements as demand has varied (you can finish a broiler quicker or slower by changing diets). Yet, feed wheat demand for ethanol production has stopped.
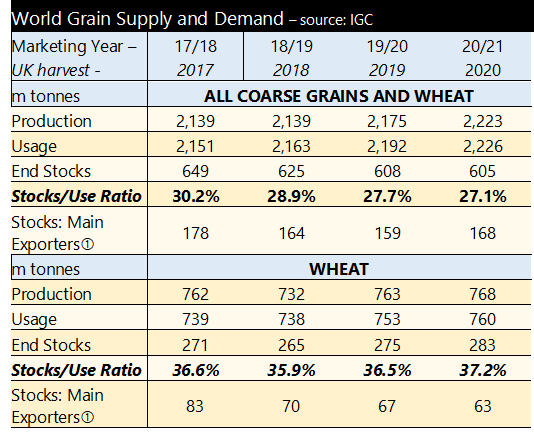
Russia and Ukraine have imposed grain export quotas, meaning prices may rise in May as these limits are hit. The overall conclusion is that milling wheat is in demand but feed wheat less so.
In the barley market, maltsters are closing sites because demand for malt has collapsed as beer consumption at home and alone is lower than in pubs with mates. Those brewers who have a market to sell to, do not have bottles to put beer in; barrels are not currently required.
The demand for oilseed has fallen as we eat less greasy take-aways and pizzas. Any requirement for OSR for biodiesel has totally dried up. Demand from the supermarkets is not being fully met either though, suggesting some issues with supply. OPEC, the oil cartel has reduced daily crude oil production but only by 9.5 million barrels as day, when consumption has collapsed by 35 million. Nobody needs oil if we’re not moving about.
New Crop
Two months ago, few would have believed that many growers in the UK now require rain. Some heavy soils are still coping well with large reserves in sub-soils but emerging spring crops require moisture at the soil’s surface and other lighter soils have become dry deeper down. The dry area extends across Northern Europe to Ukraine.
New crop wheat prices are within a couple of Pounds of contact highs, set in March. The reasons are a small crop in the ground, a wet winter and dry current conditions and some analyst’s comments suggesting the elevated bread consumption levels to continue post harvest.
The dry spell has enabled spring barley to be drilled in almost every spare corner of Britain. Few fallow fields are now evident. The potentially huge malting barley crop slowly grows, but no exports sales are being booked. Other countries nearby also have lots of spring barley, and no beer drinkers. The German Octoberfest, which attracts up to 6 million beer guzzlers has been cancelled this year. Malting quality barley will go as feed barley this year, clearly depressing the feed barley price too. The spread between barley and wheat could be considerable this autumn.
The price of beans has been falling as we enter Ramadan and the demand from our export homes slows. A large spring bean crop is in need of a good watering.


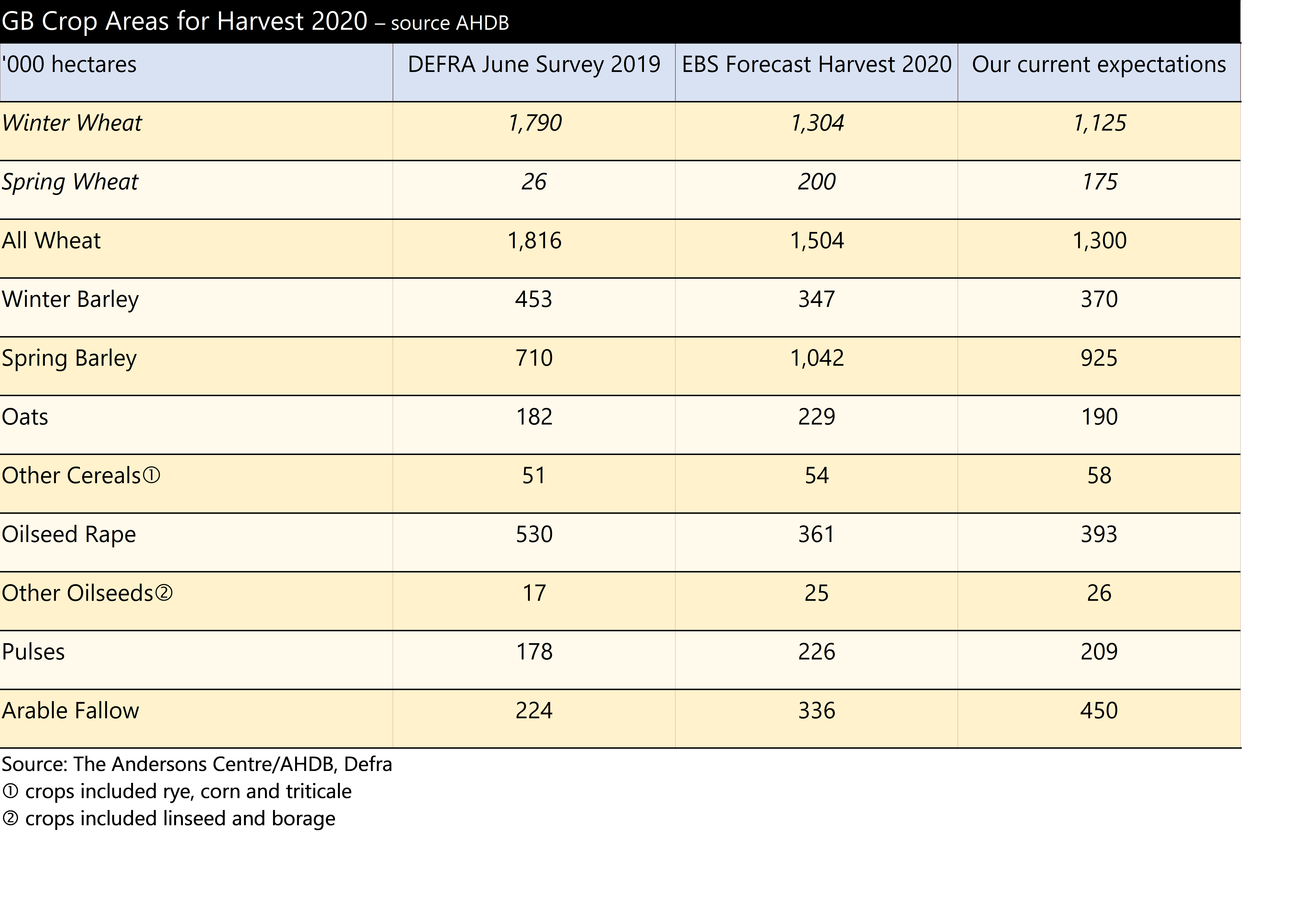 If this projection is correct, it would leave potentially the lowest wheat area planted in the UK since 1978/79, and the highest spring barley area since 1987/88. Some projections expect spring barley to exceed 1 million hectares but we are not convinced there is enough time for that to occur. Oilseed rape area might end up being the lowest since 1988/89. Even so, it still might be the highest we see again because the difficulties of growing the crop this year have been only partly because of the rain, and partly because of the flea beetle. The fallow land area we have suggested here would be the highest level since set aside was mandatory back in 2007. For 2020 autumn drilling and the 2021 harvest, we would expect a high proportion of farmers very keen to capitalise on the first wheat opportunity, possibly planting a little earlier than this year too. Hold tight for a big wheat crop next year.
If this projection is correct, it would leave potentially the lowest wheat area planted in the UK since 1978/79, and the highest spring barley area since 1987/88. Some projections expect spring barley to exceed 1 million hectares but we are not convinced there is enough time for that to occur. Oilseed rape area might end up being the lowest since 1988/89. Even so, it still might be the highest we see again because the difficulties of growing the crop this year have been only partly because of the rain, and partly because of the flea beetle. The fallow land area we have suggested here would be the highest level since set aside was mandatory back in 2007. For 2020 autumn drilling and the 2021 harvest, we would expect a high proportion of farmers very keen to capitalise on the first wheat opportunity, possibly planting a little earlier than this year too. Hold tight for a big wheat crop next year.