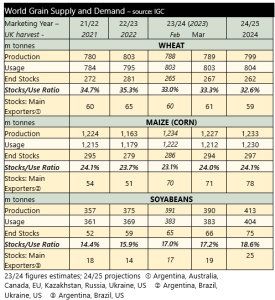
The price of grains has recently increased, driven by concerns about new crop prospects, with world supply and demand tightly balanced. In mid-April, the price of new crop UK feed wheat futures (Nov-24) reached £200 per tonne for the first time since mid-January. The increase in prices follows concern around crop conditions in key global markets.
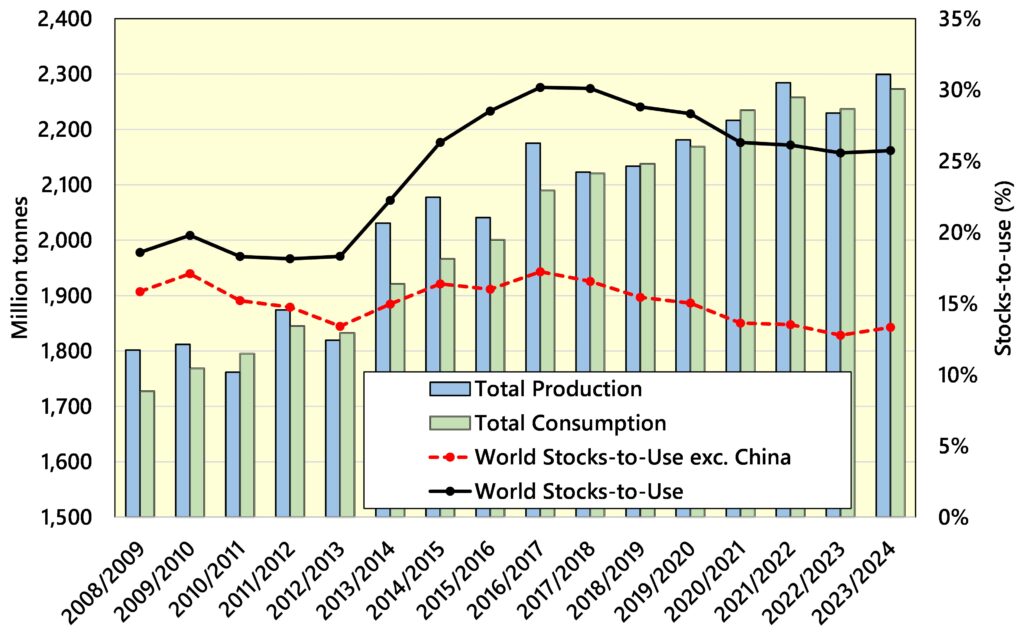
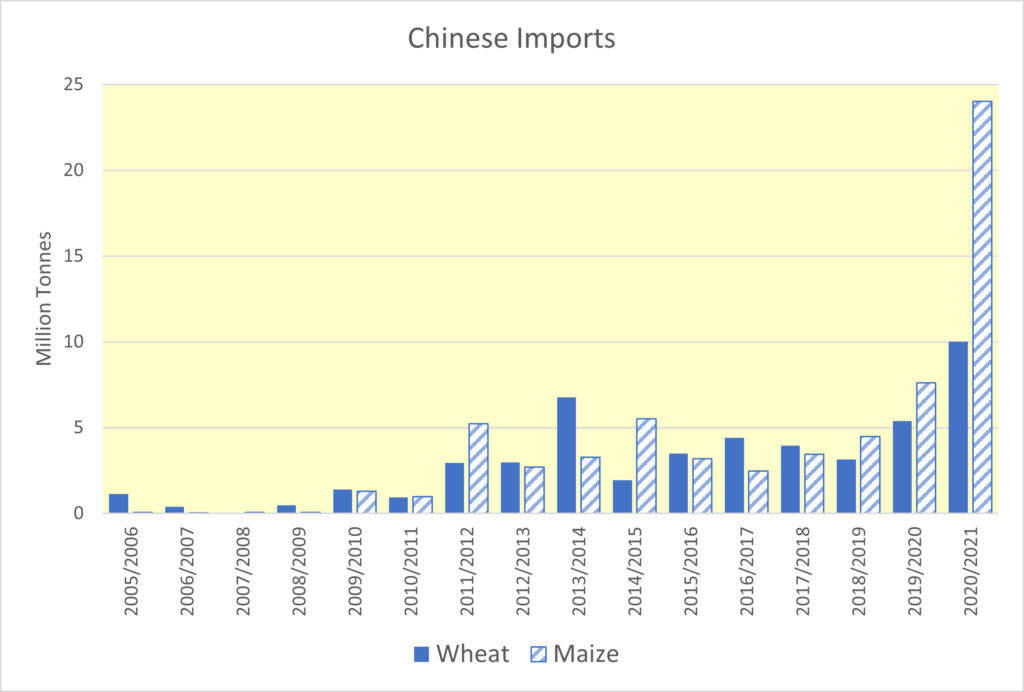
Close attention is being paid to global weather patterns, with global grain stocks following the 2024 harvest expected to rise by just 1 million tonnes, year-on-year. This is a significant decline in the International Grains Council forecast of stocks from the previous month (see table). Managed money funds still hold a large sold position in grains and oilseeds, essentially betting on prices moving lower. Recent weather concerns have led to some buying, increasing prices. Further weather concerns would lead to more fund managers reducing their short positions.
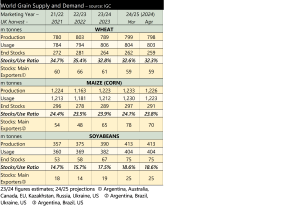
The decline in output forecasts is driven by two key factors, concern over the production of South American grain in 2023/24 (reducing carry-in stocks), and reduced North American maize acreage. Brazil has been suffering the lingering effects of El Niño, a weather pattern which brings warm, dry weather to South America. This has resulted in significantly lower soil moisture reserves. Much of the Brazilian maize crop will be planted in the coming months. With little chance of above-average rain in the coming months in central Brazil, crop prospects could yet worsen, supporting prices.
Dry weather is aiding progress with maize planting in the US, with progress ahead of the five-year average. US farmers are expected to plant 5% less maize this year, in favour of soyabeans. US weather will again be a key watch point for grain pricing this year. Also in the US, the proportion of winter wheat crops rated ‘good’ or ‘excellent’ was estimated at 50% in the week ending 21st April; down 6 percentage points since the beginning of the month. The fall in conditions is due to dry weather.
Conditions have improved in Europe. Warm dry weather throughout spring has aided planting progress in France and Germany. However, winter crop conditions are still poorer than normal. Concerns will be rising about the impact of warmer/dryer weather on winter crops. The EU Commission crop monitoring report highlights the rapid acceleration of plant development in France and the increasing prevalence of disease pressure.
In the UK, crop conditions are down significantly on previous years. To the end of March, just 34% of UK winter wheat was in ‘good’ or ‘excellent’ condition. This is down from 90% as at March 2023. A further update to crop conditions is due to be published by AHDB in May. Winter crops are looking healthier than they were a month ago, where established, although not everywhere and challenges still remain for many especially in the North of England. Furthermore, rainfall has continued to hamper spring planting efforts in the wettest regions, although progress has been made elsewhere.