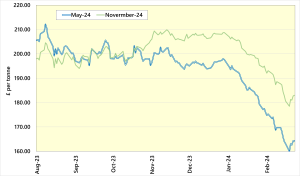
Global grain prices have been falling for much of 2024. The main driver of the decline has been ample supplies of grain anticipated to come from South America. Maize and soyabeans in Argentina and Brazil are still developing, making prices volatile in response to weather conditions. Concerns over excess rainfall in the region prompted some fund managers to cover some of their record sold positions, supporting prices in the third week of March. The role of fund managers in Chicago grain and oilseed futures markets is important for the direction of global prices. If weather conditions turn, or other funds become more or less attractive the price of grain can move quickly.
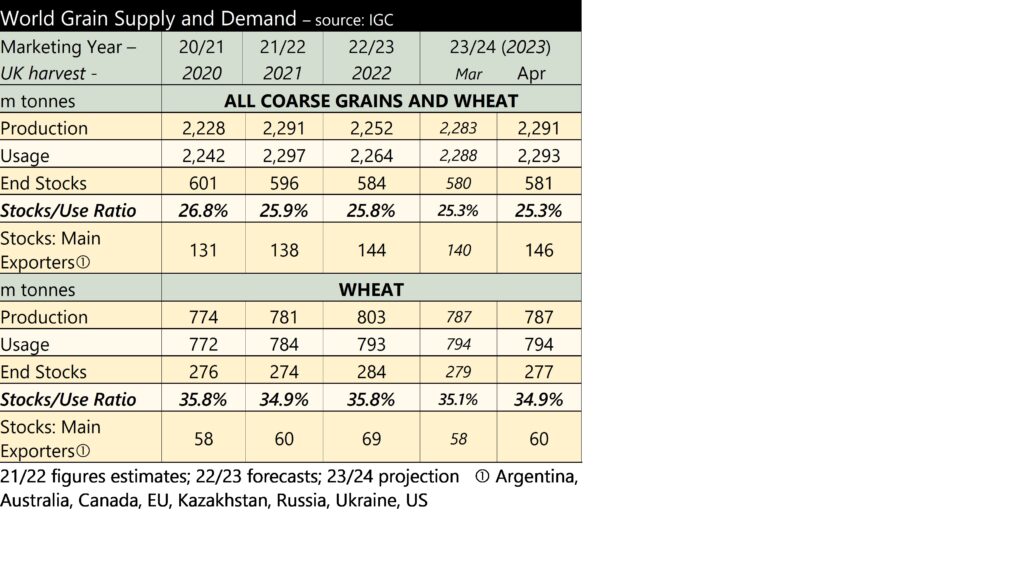
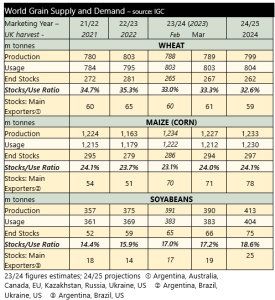
With regard to supply and demand, the International Grains Council (IGC) published its latest update for the 2023/24 season, on the 14th March. Furthermore, the IGC also published its first forecasts for 2024/25. These are shown below.
Despite cuts to global grain production in the Southern Hemisphere for the 2023/24 season, there is a greater fall in estimated consumption, resulting from reductions in feed use. As a result global stocks are forecast to increase by 10 million tonnes.
For 2024/25, the global grain and soyabean stocks are due to rise again. Whilst an increase in stocks is likely to move prices lower, the year-on-year rise is fairly small. We are still some months away from the Northern Hemisphere harvest, and it would not take a big reduction in production (forecast or actual) to move global prices higher.
For the 2024/25 season, total grains production is forecast to rise by 28 million tonnes, 10 million tonnes of that rise is wheat. Increases in wheat production are projected for Argentina, Australia, Canada and the USA. Production is expected to fall in the EU, and the Black Sea. However, usage of wheat is set to remain high and global stocks are forecast to fall by 5 million tonnes between 2023/24 and 2024/25. This may provide some specific support to wheat prices.