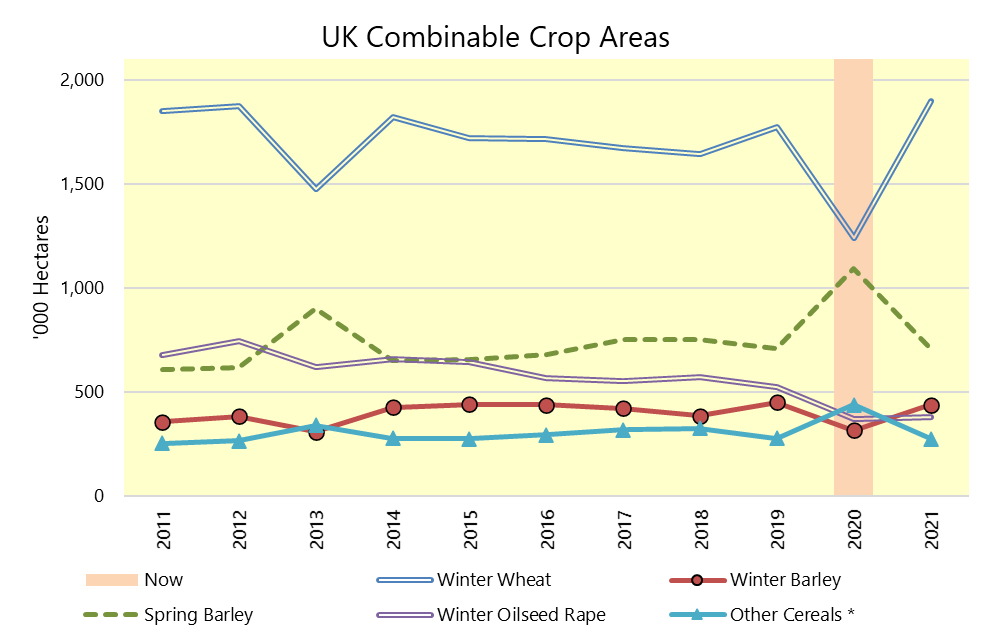
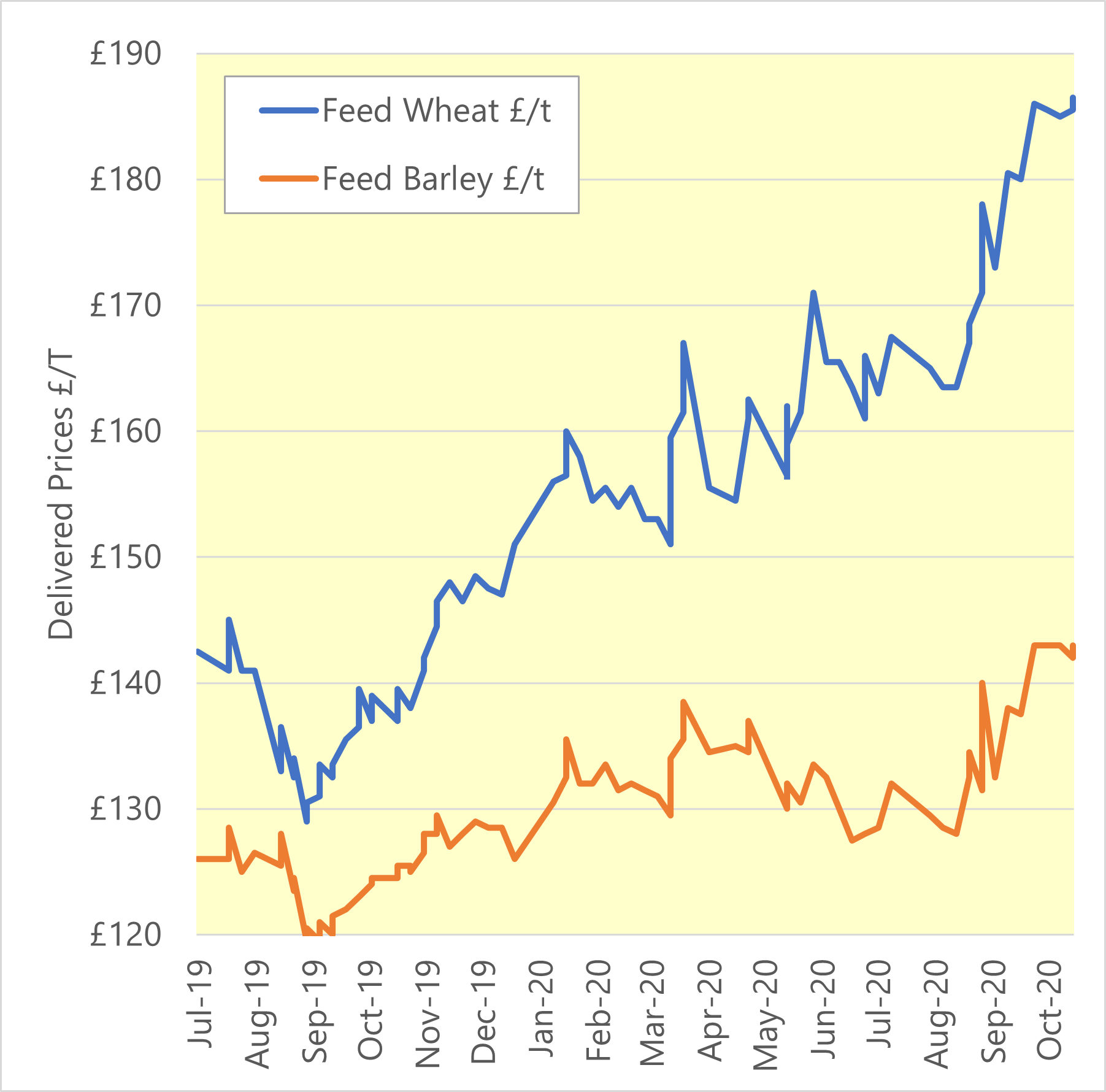
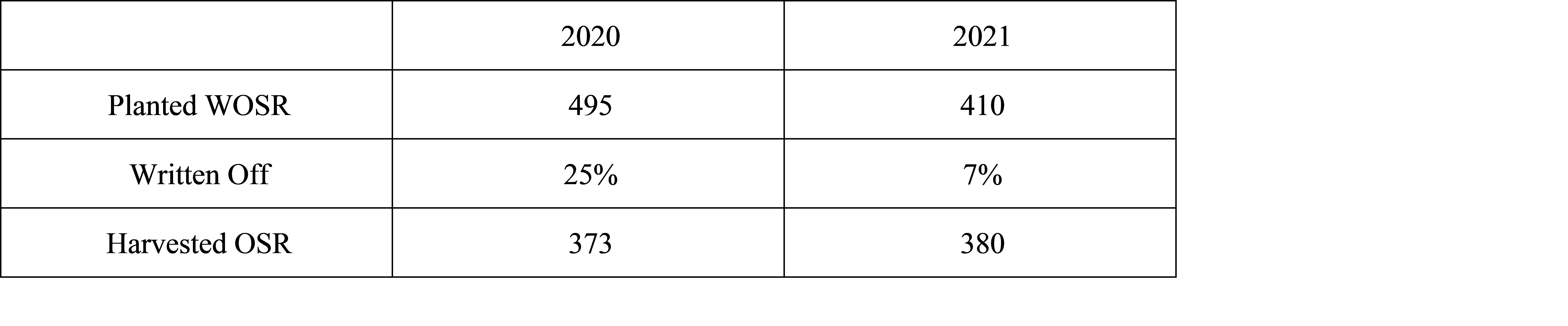
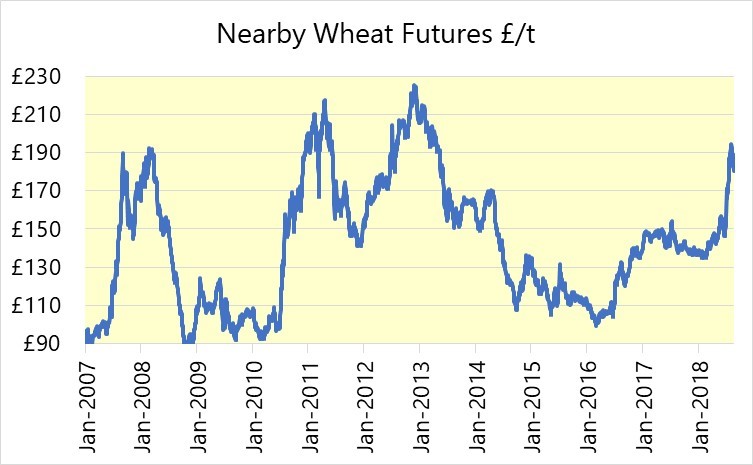
Overall
The UK grain harvest is all-but finished now and, overall, has produced excellent results. Completion by the end of August must surely be a record? The exceptionally dry and hot weather conditions have brought with it opportunities, but also challenges. Almost all the harvest will have been gathered dry, but hot. The grain drier was not needed to reduce moisture for almost all farms. Yet some used them to cool grain. Now the nights are cooling, farmers should be turning fans on to reduce the grain temperatures. As frosts arrive this will be a useful time to cool the grain further.
Numerous farmers have experienced field fires with losses of standing grain. At this stage we have no measure of how much has been lost in this way. That risk is now subsiding, but farmers must pay attention to their straw stacks. They should make more, smaller stacks than usual and preferably hidden from sight to as not to attract attention.
Wheat
Reports suggest this year’s wheat crop is excellent quality with a good yield. After the dry conditions we have experienced since June, it is easy to forget the very useful spring rains we received as grains were starting to fill. This was just as important as the ripening sunshine and the dry harvesting conditions we have had this summer.
Some reports suggest many farms have experienced greater than usual variation of protein levels within the same varieties. This means that grain sampling should be given particular attention this year. Any additional mixing might be useful if this is possible, as segregating protein levels is difficult and probably now too late to do.
New crop wheat prices fell in the latter part of August. Earlier in the month world grain markets were driven up by reports of very dry weather in the maize growing regions of the US. In addition, China was claiming a wheat crop catastrophe, with very poor conditions, suggesting fairly extreme crop failure conditions. However, it now turns out that China has harvested more wheat than last year! This reduced forecast Chinese import demand. Concerns around the Chinese economy have also dampened expectations of Chinese buying. The last few days have seen rain in the Mid-west of the US which has eased concerns about the maize crop and pulled down all grains prices.
The other global factor of note is Ukraine. Last month, we talked of how Ukraine and Russia had brokered a deal to allow Ukrainian grain exports to restart. Grain was stuck in elevators, stores and farm barns. We were skeptical it could be exported quickly or even reach the ports in many cases. In fact, almost two thirds of a million tonnes were exported in the first three weeks of August. Furthermore, the programme is continuing with expectations of 3 million tonnes going out in September. Not only does this provide grain that the world market had largely written off, but also makes storage space for the new crop. The Russian crop has also been good and exports have been high – partly making-up for the tonnages lost to the world market from Ukraine.
Barley
The UK barley crop is proving to be of a particularly high quality; most growers are thrilled with their results. However, when everybody shares such success, the market reacts. Indeed, the feed wheat:barley spread has grown to up to £20 per tonne and prices might have to decline further as UK barley is still not competing in the export market. Furthermore, the malting specification, especially for springs is so good that many crops that would have achieved malting specification in previous years will end up being fed. The malting premium has been falling as so much of the crop meets the required specification.
Reports from Scandinavia and other parts of the EU also highlight high quality and good yields, suggesting the UK malting barley crop faces some stiff competition in the marketplace this autumn.
Beans
Beans ripened almost too quickly this year. Being usually among the last crop to go through the combine, their ripening from the high temperatures was a little premature. Small bean size, especially in the spring beans, will have reduced the crop size to an extent. Shattering bean-pods has also been an issue. However, overall most farmers are relatively happy with their crops.
OSR and Drilling
The oilseed rape harvest was completed in record time. This was the case throughout Europe as well as in the UK. Not only is Europe reporting 10% more OSR than last year, but the Canadian crop is apparently half the size again from last year. Australia too, is reporting 10% more area this year. Even in Ukraine, where the crop had been partially written off, a reasonable tonnage has been harvested; more than one might have expected in the circumstances. Prices have fallen in response and are now at or near to the levels in February – before the Ukrainian war began. This is £220 beneath the highs of mid-May.
Little OSR drilling has taken place so far, with soils too dry to take the seed or allow germination. What little rain has fallen has barely softened the tops of the soils, rather drained through the cracks in most fields. Some are becoming concerned with this, although there is still ample time for rains to fall to allow satisfactory drilling and germination.