
Tag: FTA

Trade Deals Study
The Scottish Government has published a study on the impact on Scottish agriculture of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) between the UK and four selected non-EU partners, namely: Australia; New Zealand (NZ); Canada; and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). It found that these free-trade deals could have a significant negative impact on certain sectors of Scottish farming, particularly sheep. The study was undertaken, in 2022, by Andersons and Wageningen University and Research (WUR).
The study quantifies the FTA impacts on selected Scottish agricultural sectors namely: cereals (wheat and barley); livestock (dairy, beef, and sheep); and potatoes. This was done using two FTA scenarios; high and low liberalisation. These were modelled alongside the current status quo (UK has left the EU but the Trade and Cooperation Agreement (TCA) is in place). An Alternative Baseline (No-Brexit) scenario was also briefly examined.
The research was undertaken in collaboration with Wageningen University and Research (WUR) and used a combination of MAGNET, a computable general equilibrium economic model to assess the individual and aggregated impacts of each FTA, as well as desk-based research and interviews with industry experts based in Scotland, the UK, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, and the Gulf region.
Key Results
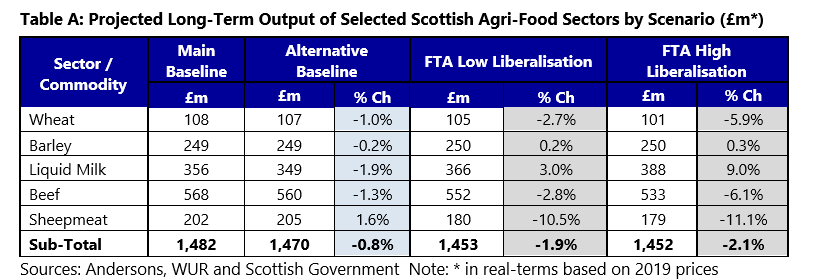
- Impact of the selected FTAs is generally limited, but significant in some sectors: as Table A depicts, the projected long-term impact of the FTAs on Scottish output is relatively small in most cases. The exceptions are sheepmeat, where output is forecast to fall by around 10.5% to 11% under the Low and High Liberalisation scenarios. Beef and wheat are also projected to fall (both by around 3% to 6% depending on the scenario). Conversely, liquid milk output is forecast to grow by 3% to 9% in value terms, indicating significant FTA opportunities for dairy products. Barley is forecast to show a small long-term gain.
- Cumulative impacts of future FTAs will be more significant: although the aggregated impact of the selected FTAs is relatively limited, the cumulative effect of multiple trade deals over the longer term should not be underestimated. This is especially so if the UK agrees FTAs with agricultural powerhouses such as the US and Mercosur (including Brazil and Argentina).
- FTAs with Australia and NZ are main drivers of declines Scottish sheepmeat output: the new FTA is seen by many as a strong signal for NZ businesses to recapture trade with the UK, which was lost when the UK joined the EEC. Australia will also be keen to increase sheepmeat exports to the UK.
- Beef sector will come under pressure but some opportunities also exist: whilst imports from Australia and NZ will create more competition, a trade deal with Canada is likely to generate some export opportunities. Given the brand recognition of Scotch beef, it should be relatively well-positioned to exploit such niches. That said, safeguarding domestic sales, particularly to UK retailers, from overseas competitors will remain most crucial.
- The FTAs with Australia and NZ set important precedents: the recently agreed FTAs with Australia and NZ give important signals to other countries on what the UK is willing to cede in trade negotiations. Therefore, the standards that the UK is willing to accept for imports is pivotal, especially as other FTA partners will likely push for more concessions during negotiations. Any significant changes to standards relating to food safety and hygiene, the environment and animal welfare will have major implications for Scottish produce. This is not just on the home market, but overseas as well, especially in terms of highly-renowned brands such as Scotch Beef.
- FTA opportunities for dairying the dairy sector is best positioned to see export growth, particularly to the GCC, where Scottish dairy produce has already gained traction in high-end segments. UK exports to GCC in 2018-20 are valued at £38m and could rise by as much as 49% in a High Liberalisation scenario. Opportunities theoretically exist to export to Canada, but, as it is highly protectionist, sales are likely to be limited to select niches.
- Long-term impact of Brexit is deemed to be limited: Table A also shows relatively small differences in output under the Main Baseline (incorporating Brexit) and the Alternative Baseline (No-Brexit scenario). Although seed potatoes were not modelled, the loss of the EU markets for Scottish seed potato exports is significant and the restoration of this market access is a key goal for the sector. It should also be a primary objective for policy-makers.
- Significant Farm Business Income (FBI) declines: of up to 60% in some sectors, in both the Main Baseline and FTA Scenarios in comparison with the Base Year (2019/20) although the differences between the Main Baseline and FTA scenarios are quite small. This is chiefly linked with declining prices.
- New FTAs to have negligible impact on potatoes: industry input suggests that the new FTAs will have minimal impact on seed potatoes’ profitability. Instead, the impact of the loss of the EU market for Scottish seed potatoes is estimated to have led to a decline in seed potato prices of approximately 4%. Restoring market access to the EU27 and Northern Ireland is a priority for the sector.
Overall, the findings that more pressure will be exerted on the Scottish (and UK) beef and sheepmeat sectors are unsurprising as Australia and New Zealand are widely regarded as significant and highly competitive players on the world markets. That said, the projected extent of declines on output is perhaps not as pronounced as some might have feared, although the declines are still significant. The report also suggests some opportunities for dairy products, particularly in the Gulf region.
The Summary Report is available on the Scottish Government website via: https://www.gov.scot/publications/analysis-impact-future-uk-free-trade-agreement-scenarios-scotlands-agricultural-food-drink-sector/

UK/Australia FTA Analysis
On 13th April, the Trade and Agriculture Commission (TAC) published its advice to the International Trade Secretary (Anne-Marie Trevelyan) on the UK-Australia Free Trade Agreement (FTA). This is the first such piece of advice that the TAC has compiled and its findings have been presented to Parliament to aid its discussions on ratifying the trade deal.
The Terms of Reference for this TAC report focused on assessing whether, in relation to agricultural products, the new FTA is consistent with the maintenance of UK levels of statutory protection in relation to three key areas;
- Animal or plant life or health,
- Animal welfare, and
- Environmental protections
The TAC report addressed three questions which are set-out below, with the TAC’s conclusions on each question summarised in italics.
- Whether the FTA requires the UK to change its levels of statutory protection in relation to the three areas above? The TAC has found that the FTA does not require the UK to change its existing levels of statutory protection in relation to animal or plant life or health, animal welfare, and environmental protection.
- Whether the FTA reinforces the UK’s levels of statutory protection in these areas? The TAC’s view is that the FTA reinforces the UK’s statutory protections in the areas covered. It cites two reasons. First, the FTA contains environmental and animal welfare obligations that require the UK to maintain its statutory protections in the areas covered. Second, these obligations also ensure that Australia will not gain a trade advantage by lowering its standards of protection or not properly implementing its domestic laws in the areas covered.
- Whether the FTA otherwise affects the ability of the UK to adopt statutory protections in these areas? The FTA does not otherwise affect the UK’s ability to adopt statutory protections in the areas covered. It does not restrict the UK’s WTO rights to regulate in these areas, and potentially enhances these rights in some respects. However, the UK is able to adopt decisions under the agreement, together with Australia, that may constrain its freedom to regulate in future. Therefore, the TAC believes that it is important to ensure that the UK’s import control systems are properly resourced to manage increased imports under the FTA.
The TAC report also examines a number of other issues which have caused concern. These include;
- Pesticides: the TAC finds that the FTA is likely to lead to increased imports of products from Australia using pesticides which are banned in the UK. Whilst there are Commonwealth laws concerning the environment and pesticides use which Australia has obligations under, these laws are limited.
- GMOs: although there is negligible GMO production in the UK, it is currently legal to import and market GMO products, provided that it is labelled as such. The TAC suggests that it is possible that GM canola oil (from oilseed rape) from Australia could be imported in increased quantities under the FTA. However, imports of cotton and safflower, the other two major Australian GMO crops, will not be imported in increased quantities. Furthermore, the UK’s WTO rights to regulate the import of GM products remain the same under the FTA.
- Hormone-fed beef: the importation of such products would remain illegal in the UK and the FTA does not change this legal position.
- Feedlot beef: would inevitably increase under the FTA and it would be difficult under WTO law for the UK to impose restrictions.
- Hot branding: whilst legal in Australia, the UK requires electronic identification of cattle for export to UK, thus hot branding is unnecessary.
- Slaughterhouse CCTV and stunning: CCTV is not required in Australia and meat from these premises could not be restricted from being imported into the UK. The TAC also state that it is illegal to export meat from non-stunned animals so such meat should not enter the UK as a result of the FTA.
- Mulesing: is the practice of removing wool-bearing skin, without pain relief, from the buttocks of a live animal and is done by Australian sheep farmers to prevent flystrike. The TAC found that the likelihood of mutton from mulesed sheep being imported into the UK is negligible but there is a “much higher chance” of wool from mulesed sheep being imported.
Overall, whilst the TAC has found that whilst imports using the most controversial practices (e.g. hormone-fed beef) will continue to be prohibited, there is scope for increased competition from Australian imports, particularly beef, lamb and wheat, which sometimes will be produced to lower animal welfare and environmental standards. However, it is worth acknowledging that Australian beef and lamb is currently achieving high prices in the global market (particularly Asia), thus making exports to the UK somewhat less attractive, at least in the short-term. Of course, in the long-term, supply/demand and geopolitical influences can change the market situation significantly. Importantly, the UK-Australia FTA creates a precedent for other trade deals. Whilst this FTA alone does not alter the playing-field that significantly, the cumulative impact of trade deals will have a much more influential impact.
For full detail on the TAC’s advice, please visit: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1068872/trade-and-agriculture-commission-advice-to-the-secretary-of-state-for-international-trade-on-the-uk-australia-free-trade-agreement.pdf
Also, please note that the TAC has launched a similar consultation on the UK-New Zealand trade deal. More detail via:
